We use the latest advanced technology for eye disease detection and documentation. The clinics screen for a range of eye conditions including glaucoma, macular degeneration, cataract, diabetic retinopathy.
Our optometrists and students spend time with you to establish a complete picture of your vision, your visual requirements, overall health and lifestyle.
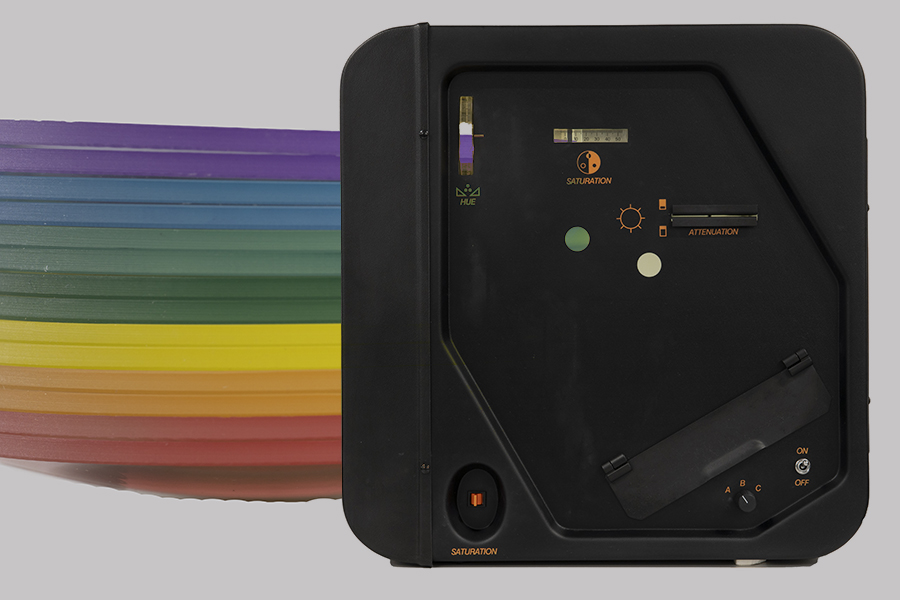

The Intuitive Colorimeter specialises in refining the coloured tint required for a person who is affected by ‘visual stress’, a condition that can contribute to difficulties with reading.
The finalised colour is different for each person with over 100,000 colour combinations available.
It is possible to order spectacle lenses with the finalised colour.
Students and adults with dyslexia may also experience visual stress and can benefit from coloured lenses in some cases.
.jpg)
The Goldman tonometer is the gold standard method used to measure the eye's pressure.
It is used by ophthalmologists (eye specialists) and optometrists to monitor the pressure of the eye. We put some simple drops in your eye and use a small probe with blue light to exactly measure the pressure of your eye.
If the eye pressure increases it can lead to glaucoma.
At every eye examination, we examine your visual field to check the extent of your peripheral vision. Many eye conditions can affect your visual field.
The National Optometry Centre uses the latest Zeiss technology to screen your vision using the FDT machine. Where a more detailed examination is required, we use the Humphrey VFA. This is the ‘gold standard’ visual field machine used by eye hospitals to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma.
We also use the Humphrey VFA for Esterman field testing to assess a driver’s visual field for Group 2 driving license screening assessments.

The iCare Tonometer is the latest technology to measure your eye pressure and there is no puff of air.
Your eye pressure is measured at your visit to the National Optometry Centre. If your eye pressure goes up it could lead to glaucoma.
The Oculus HMC Anomaloscope is a computer-controlled instrument is the “gold standard” for diagnosis of both the type and extent of colour vision deficiency (CVD). It identifies the four commonest CVD types as well as four rare types.
In the more commonly used mode, it presents variable mixtures of red and green light which patients match to yellow light. Patients with CVD use abnormal mixtures of red and green light.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina. The scan allows us to see the individual layers of the retina, with measurements seen in micrometers.
At your visit, we take scans of the macula and the optic nerve. The macula scan checks the accurate point of vision for conditions like macular degeneration, epi-retinal membranes, and macular holes. These are changes that are very difficult to detect or monitor with more traditional imaging systems.
The optic nerve scan measures the thickness of the nerve fiber layer as it enters the nerve. In glaucoma, as the nerves die off the thickness of the nerve fiber layer reduces. The OCT scan allows us to compare your optic nerve thickness against normalised measurements to allow us to see if you have glaucoma.
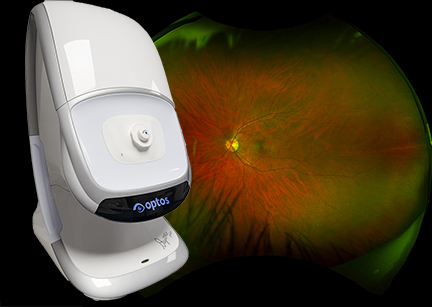
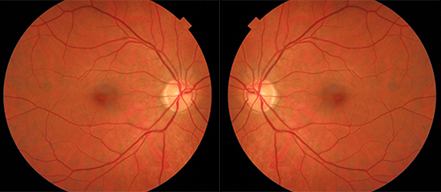
Standard imaging techniques only capture about 18% of your retina at one time.
Optos or Optomap ultra-widefield retinal imaging is the only technology that captures more than 80% of your retina in a single image.
An optomap image provides a bigger picture and more information to allow us to pick up the earliest signs of a retinal detachment.
We have an Optos Daytona machine at the National Optometry Centre which allows us to see more of your retina than other imaging machines.
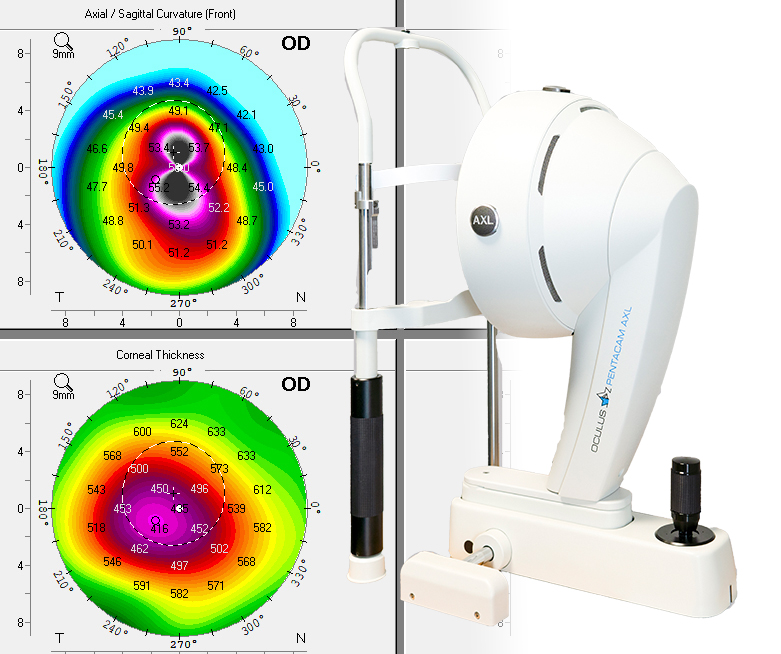
The cornea is the eye's clear, protective outer layer, which focuses light into the eye. A steeper cornea has a higher power while a flatter cornea has a lower power.
We use topography to scan the cornea and it is an essential part of specialist and RGP contact lens fitting.
These machines map the surface curvature of the eye and we use them to monitor and measure changes in the shape and condition of the cornea.
Corneal topographers allow us to detect conditions like keratoconus and monitor an eye after laser refractive surgery.
We have a Medmont and Pentacam topographer in our contact lens suite at the National Optometry Centre.


